Looking at a few different options for GRC software? Here are some product and support criteria to consider when evaluating potential vendors.
Implementing governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) technologies is an effective way to move away from spreadsheets and shared folders, but given the number of GRC software vendors, it can be difficult to choose. Vendors often claim functionality in many areas, even though their actual capabilities may be quite limited. If you’re looking at a few different options for GRC software, here are some of the features and capabilities you should consider.
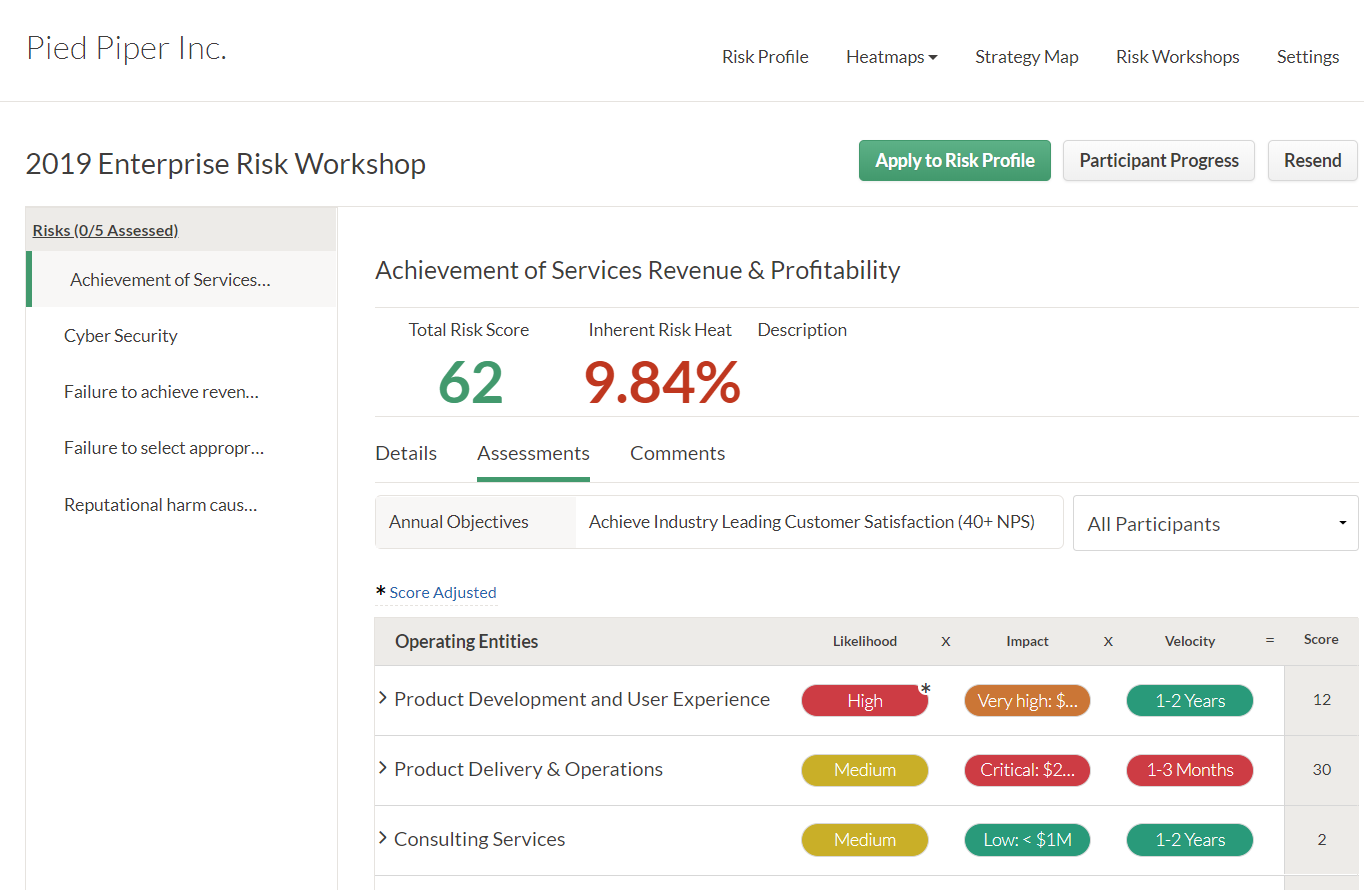
Risk assessments and weightings
How easy is it to quantify and rank your risks? Some GRC solutions let you assign a score to each risk, as well as apply a weighting so that you can rank your risks for impact against others. This small feature can really help you prioritize the areas of your business that need to be tackled first.
Conduct risk assessment voting workshops within HighBond to determine risk scores.
Risk database
Can your organization’s risks be easily shared and understood? A strong GRC solution simplifies how you identify and communicate risks (e.g., through a centralized database of risks). This gathers common risks and provides enough detail so that users in different business areas can easily understand the impact of each.
Controls database
How well can you link your risks to your controls? You want a solution that can map each risk to a corresponding control. The system should allow the control process to be described in enough detail and provide links to fully detailed documentation.
Exception management and workflow
Managing exceptions can be tedious. The easier the software can make it, the better. Your solution should support detailed and complex workflows, including how exceptions and results are routed, and how procedures are escalated.
“How many data sources can you connect? You should be able to connect effortlessly to multiple different data sources, and automate data extraction routines.”
Analytics libraries
Can you store analytics for reuse another time? Automated and repeatable analytics used in audit and compliance testing should be maintained in secure and efficiently structured libraries.
Ad hoc analytics
The ability for non-technical auditors and compliance specialists to perform ad hoc analysis of detailed data is increasingly important in many GRC processes. So, is the software usable by third parties? Going with a user-friendly solution puts you one step ahead of this potential challenge.
Data connections, access, and extraction
How many data sources can you connect? You should be able to connect effortlessly to multiple different data sources, and automate data extraction routines.
Data cleansing and manipulation
Extracted data usually requires some form of cleansing and restructuring in order for it to be used in GRC processes. Make sure this process makes sense to you in whichever software you choose.
Visual analysis
Does the software help you understand the data easily? Easy-to-use visual analysis capabilities are important during the audit planning and risk assessment phases of internal audit, as well as in risk and compliance activities.
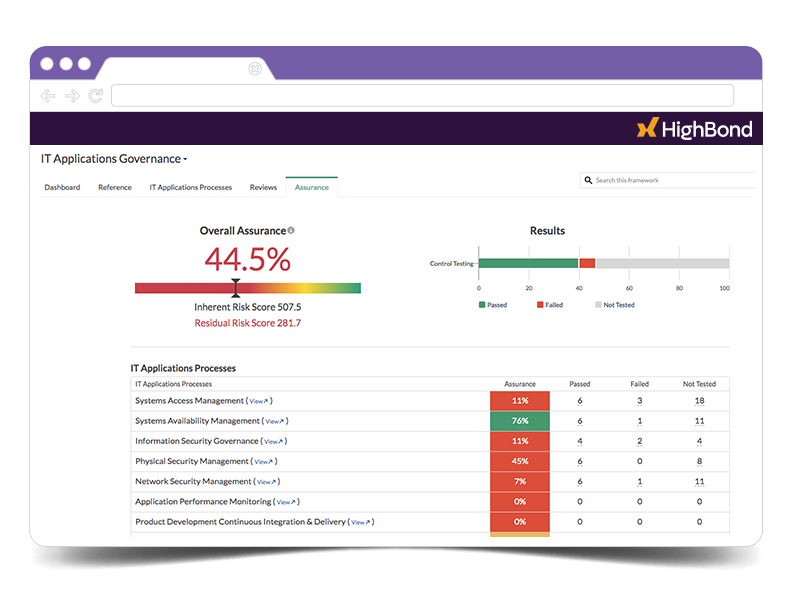
Reporting and dashboards
What level of reporting can you achieve? The ability to produce flexible reports on multiple aspects of GRC processes is clearly important, and particularly in terms of providing dashboard views of the status of risk assessments.
With HighBond, generate executive dashboards, track KPIs and cycle times, manage issue life-cycles, and customize graphs, fields, and outputs.
Script building and automation
Automating analytics for control testing and risk identification is critical to data-driven GRC processes. The solution should support the ability to perform complex data manipulation and processing, as well as user interfaces for parameter input to automated analytics.
Scheduling analytics
Can you schedule the ongoing processes you need? Many automated analytic tasks, including both data extraction and detailed monitoring and testing, need to be scheduled to run according to a variety of parameters including date, time, and the availability of specific data files.
Security
How many layers of security exist for accessing and sharing your confidential data? Access privileges, protection against data breaches, and strong data encryption are essential parts of assessing a potential GRC solution.
Scalability
Will the software that works for you now continue to work for you as your data grows? Data-driven GRC processes typically involve very large amounts of data, often from multiple sources, and with complex processing requirements. Software needs to be able to efficiently and reliably handle increasing data volumes.
Integration with other technologies
Ideally, one software platform is able to support multiple aspects of GRC processes; however, there can be times where GRC software needs to connect closely with other specialized software that you might use, such as financial risk management software.
Mobile device support
Can the software be used on the go? You might have auditors and compliance and control specialists that need to initiate processes and view results while traveling and using multiple devices. Consider whether your vendor supports mobile devices.
Technical support
The availability of very effective technical support is a key component in successful GRC software, particularly during the initial implementation phase.
Weighting vendors
These are some general features and considerations to help evaluate GRC vendors, but don’t forget to include your own organizational requirements. These include cost, vendor reputation, and product strategy (e.g., can the technology grow with your business needs?).
Does this seem like an overwhelming amount of information? A good way to assess it all is to create a detailed table with all of your GRC requirements and considerations, and then add weightings/scores for each vendor on each of the essential criteria. Then you’ve got a data-driven evaluation to help guide your decisions!
Get an overview of HighBond‘s features.
eBook:
Machine learning for governance
Explore this evolving technology. Learn how machine learning:
- Analyzes huge amounts of structured and unstructured data.
- Meets increasing regulatory requirements.
- Detects and prevents fraud.
- Automates critical processes and delivers the answers that drive strategic change.